Introduction
The growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years has been nothing less than spectacular. From traditional looms to factories powered by technology, the industry has experienced a shift, which has attracted the attention of international markets and local investors. If you have noticed a tremendous change in the working style of the Indian textile industry, you’re absolutely right.
This blog post takes you through the key events that have happened in the industry from 2014 to 2024. You will learn about production changes, rising exports, workforce expansion, and major government interventions. Whether you are analysing the textile market in India or exploring growth trends in the textile sector, this breakdown provides you with the complete view.
We’ll present detailed, comprehensive textile production statistics in India to indicate the economic and policy milestones, as well as to demonstrate how the Indian textile industry is gaining momentum both on a national and global scale. You’ll also find expert insights and trusted resources from textiletrendshub.com, your trusted source of all things fabric, fashion, and future.
By the end of this read, you will not just have an idea of the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years but also the future of one of the oldest yet most dynamic sectors of India.
The Pre-2014 Scenario: Setting the Stage for Growth
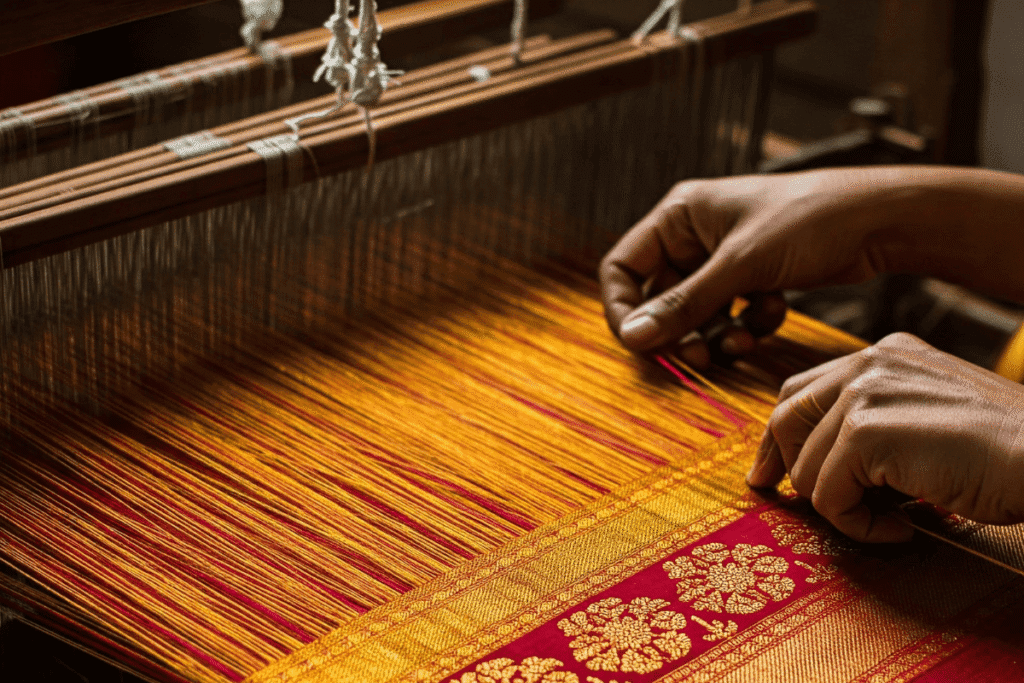

To truly understand the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years, it is perhaps necessary to first see how it all started. Prior to 2014, the Indian textile industry had a strong foundation in its history of craftsmanship but no modernisation or international competitiveness by current standards.
The scene was dominated by the traditional textile sector, particularly in the rural setup. The industry owed much to handlooms, khadi, and production through artisans. Yet, this sector was primarily associated with the problem of using old technology, low productivity, and lack of scalability despite the high cultural value.
The success of much of the industry before 2014 relied on exports. Although India was present in the international markets, it relied more on the basic cotton products and low-cost labour. The performance before 2014 was good, not impressive—it had the potential but lacked the pace and the organisation to challenge the global giants such as China.
The other significant constraint was that textile manufacturing in India did not have a developed infrastructure. The units were mostly small-scale and decentralised in the disorganised sectors. This caused discrepancies in quality, cost and the efficiency of the supply chain.
Looking back, this period set the foundation for transformation. The traditional strengths remained, but the need for modernisation became clearer, setting the stage for the impressive growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years that we see today.
Production and Output Growth of the Textile Industry in India in the Last 10 Years (2014–2024)
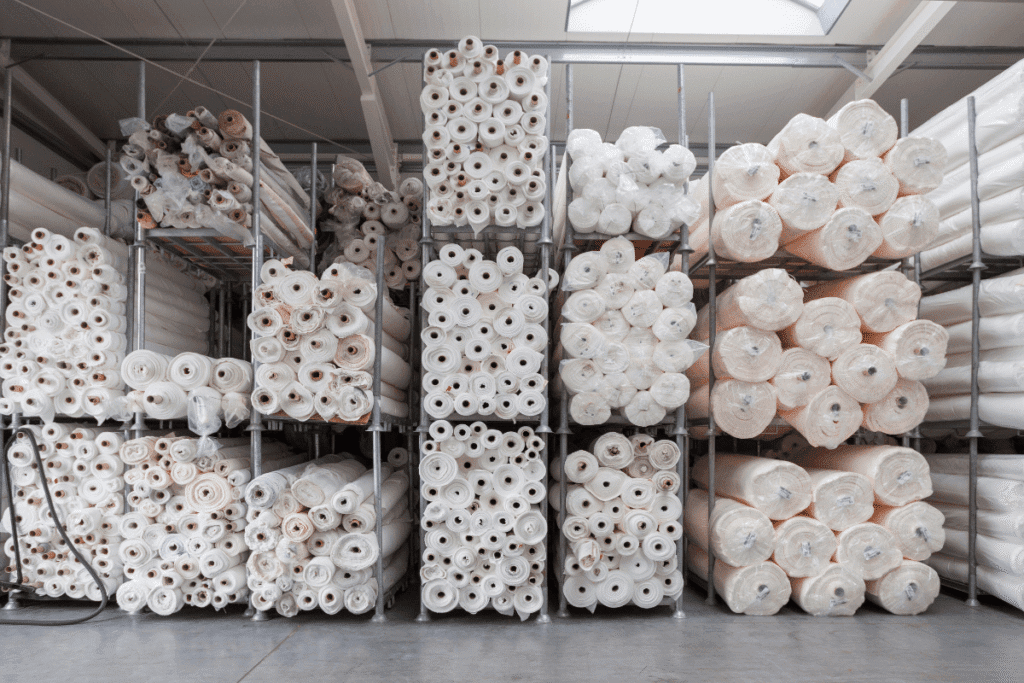

The boost in production and output in the textile industry in India is a manifestation of the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years. Whether it is yarn or ready-made garments, the sector has always increased in terms of quantity as well as quality.
The textile industry in India experienced a great spur in the level of output between 2014 and 2024. According to government and industry sources, cotton yarn production has grown significantly from around 4,000 million kilograms in 2014, reflecting India’s expanding textile capacity. Production of fabric increased in cotton, man-made fibres and blends, which implies a shift in the domestic demand and export preparedness.
The spinning and weaving units, which were initially marred with age-old equipment, have been considerably modernised. Government schemes such as TUFS (Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme) have seen units move to automation, which increases speed and precision. A majority of India’s spinning units have adopted modern technology, up from limited automation a decade ago, thanks to schemes like TUFS.
Textile production statistics in India also indicate the increasing garment production. India has significantly increased its cloth production between 2014 and 2024, showing a notable increase in output capacity over the last decade. These figures demonstrate output trends that indicate India’s desire to become a textile power in the world.
The textile sector in India has specifically increased its technical textiles and non-woven fabrics production, owing to the new age demand in medical, automotive, and agriculture applications. This has diversified growth, which has made India a stronger nation in terms of industrial fabric, both literally and economically.
The increase in output is not merely quantitative but also qualitative in terms of modernisation, efficiency, and preparedness for the future. India has ramped up sustainable textile practices such as eco-friendly dyeing, organic yarns, and solar-powered production, with strong government backing.
Here at textiletrendshub.com, we constantly monitor these production milestones and provide real-time information on the textile production statistics in India. You might be an investor, a student, or a manufacturer, but you should know these spinning and weaving unit enhancements and output indicators to complete the image of the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years.
Employment and Workforce Impact in the Indian Textile Sector
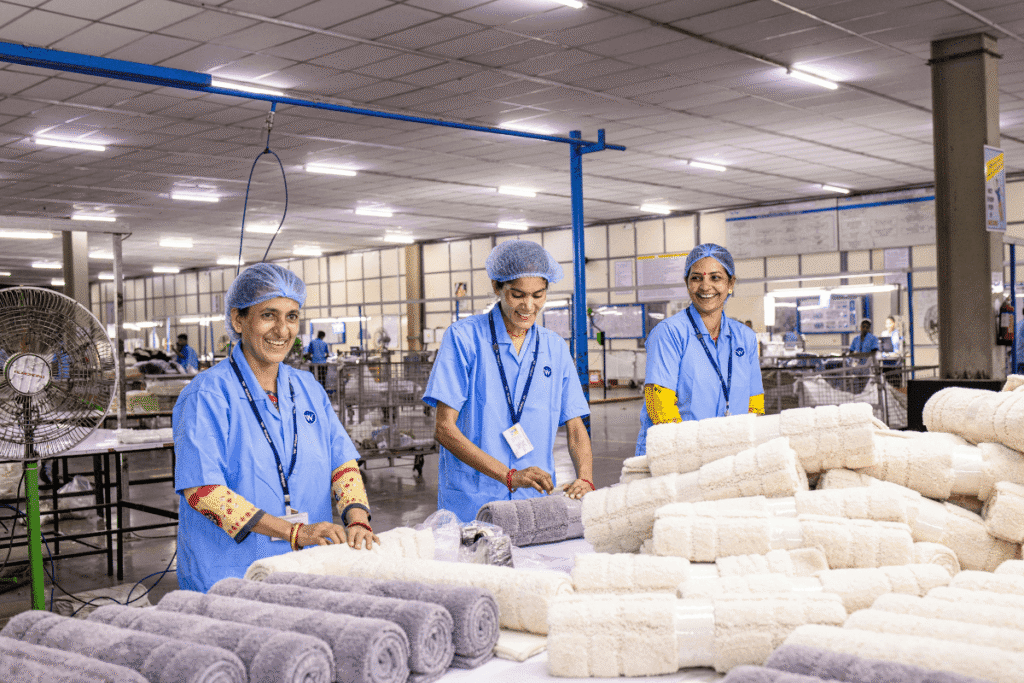

The growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years has had a direct impact on the creation of employment in the country. The sector is still among the biggest job creators in India, after agriculture. Whether it is the talented artisans or the machine operatives, the increasing number of the workforce has formed the backbone of the economic contribution of the industry.
Employment in the textile sector has increased not only in size but also in variety. Rural and semi-urban centres where modern textile production has hybridised with traditional crafts have contributed a large part of this growth. Especially, women have taken a central role. Their involvement in spinning, weaving, embroidery and garmenting has increased, leading to the emergence of improved livelihoods and empowerment opportunities. In most of the states, women have come to constitute over 60% of the shopfloor-level workers in the industry.
The growth of textile clusters in states such as Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and West Bengal is one of the biggest employment boosters. These clusters act as hubs of manufacturing, talent creation and export. Due to the growing demand for textiles in the global market, these clusters have multiplied their activities, which has resulted in higher employment in the textile industry and growing income levels at the grassroots.
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) have been important in preserving textile jobs as well. As a matter of fact, the MSME textile jobs have constituted the mainstay of the decentralised textile production. Whether it is handloom units in the Northeast or powerloom centres in Bhiwandi, small businesses have employed a huge population of workers and backed local economies.
The general size of the workforce in the sector has been estimated to be growing by different bodies of the government and industry. The growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years has created over 45 million direct and 60 million indirect jobs, and this figure is likely to keep going up with the aid of automation and global market demands.
There are also huge disparities state-wise. Tamil Nadu is the leader in spinning jobs, and Gujarat in synthetic textile processing. Handloom and embroidery work have increased in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, particularly in the textile clusters there.
After all, the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years is not only an economic tale but a human one as well. Each job possibility means a family with a better perspective, a weaver preserving tradition, and a young employee who acquires future skills.
At textiletrendshub.com, we are still keeping track of the developments of this employment landscape with real-life stories and policy changes that will be of interest to this workforce and the industry.
Export Performance of Indian Textiles

The export sector is one of the clearest indicators of success when it comes to analysing the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years. India has always been one of the top textile exporters worldwide, exporting raw cotton and yarn to high-fashion fabrics. This constant growth of Indian textile exports indicates increased capability, diversity, and adaptability in international markets.
In the last 10 years (2014–2024), India has sold textiles worth billions of dollars to more than 100 countries. The top textile export destinations include the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Bangladesh, and the UAE. Synthetic fibres, home textiles, readymade garments and Indian cotton yarn have become immensely popular in these regions. Though the supply chains were affected even in times of the COVID-19 pandemic, India recovered fast because of the high demand and its solid production premises.
What is also interesting in the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years is the way the nation has begun fighting with powerful giants such as China and Bangladesh. India has also overcome competition in certain of its segments, such as home textiles and cotton yarn. A recent comparison of India vs. China textile exports suggests that China still holds the driver’s seat in synthetic fibre exports; however, the natural fibre export by India has captured the driver’s seat in certain markets.
Another factor that has led to this export boom is the requirement for Indian textiles in the global market, especially the need for eco-friendly fabric and sustainability in production. The conventional advantages of India, such as organic cotton and handicraft skills, have gained a lot of commercial value as international consumers and buyers focus on ethical sourcing.
At the textiletrendshub.com, we have undertaken detailed export analysis, including the product category, growth trend, and future prospects. It is clear that export potential has emerged as a big pillar in the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years, in terms of volume as well as in terms of value.
With the global demand being ever-changing, India’s adaptability and diverse product offerings make it a leader in the export of textiles. Whether it is the shifting trade routes or the birth of new digital supply chains, exports will continue to be a pillar of the Indian textile success story.
For a deeper look at how textile exports from India have powered industry growth, explore our detailed blog post on export performance, product categories, and future trends.
Domestic Consumption & Retail Market
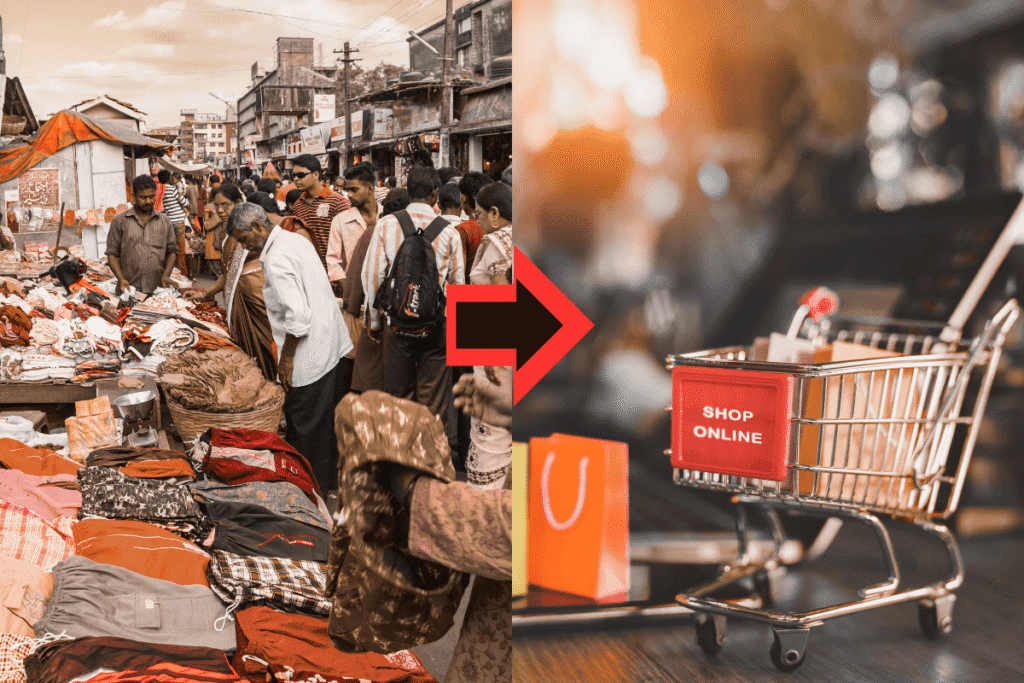

A bustling domestic market has also been a very strong driver in the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years. With the changing lifestyle of the consumers and increased urban incomes, the textile retail business in India has evolved into a high-demand and high-innovation category. The period between 2014 and 2024 was characterised by the increasing brand consciousness of Indian shoppers, their tendency to follow trends, and an increased level of online shopping.
Among the most significant changes that facilitated the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years was the emergence of online sales. Customers, even in tier 2 and 3 cities, could access the latest styles with the ease of e-commerce giants such as Myntra, Flipkart, and Nykaa Fashion. The Indian textile market was transformed by this digital wave, and the brands are prioritising collections that are digital-first, launching them through influencers, and creating personalised fashion experiences.
Also crucial was the growth of organised retail areas and fashion-forward malls in India. The urge for fast urbanisation and fashion-conscious youth raised new retailing needs, and globally adapted local fashion trends increased sales in all categories, from ethnic wear to athleisure styles.
Specifically, the apparel industry growth in India has played a major role. More disposable income and the shift of social norms stimulated the market for everything, including office attire and eco-friendly fashion. In the meantime, both local and global brands reacted by offering tech-facilitated shopping and eco-friendly lines to attract changing buyer interest.
All these trends contribute to the impetus of the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years, which shows no signs of slowing down.
Government Schemes and Policy Support

It is a fact that one of the greatest catalysts for the expansion of the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years has been the solid and steady government support for the textile industry. Through policy changes, direct incentives, and everything in between, the Indian government has been instrumental in crafting the success of the industry in the modern day.
The key attraction is the PLI scheme for textiles, unveiled to boost the production of man-made fibres (MMF) and technical textiles. This initiative has a budget of 10,683 crores, which has now incentivised massive investments in advanced textile manufacturing. It also seeks to brand India as a global source of high-value textiles—a move that aligns perfectly with the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years and supports the long-term sustainable development of the sector.
The domestic manufacturers have also gained international limelight through the Make in India textile initiatives by the government. The Make in India textile initiatives have triggered employment and innovation in the industry by promoting indigenous production and export competitiveness, which has brought buyers and investors into the industry globally.
Another game-changer is the initiation of PM MITRA Parks (Prime Minister Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel). These parks are expected to offer global-standard textile infrastructure, lower costs of logistics, and integrated value chains, further boosting the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years.
Backing up all these initiatives is the developing National Textile Policy, which follows the trends of global trade but also promotes innovation, sustainability, and digitalisation. These structures have created a climate of expansion, collaboration and investment, which directly drives the impetus witnessed in the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years.
As reforms and government policy interest continue to be showered on the sector, it is obvious to note that the government support for the textile industry will continue to be a strong pillar in future prosperity.
To learn more about government schemes and policy support for the textile industry in India, check out our detailed guide: Government Schemes for the Textile Industry in India: Benefits, List & How to Apply (2025).
Technological Advancements and Modernisation
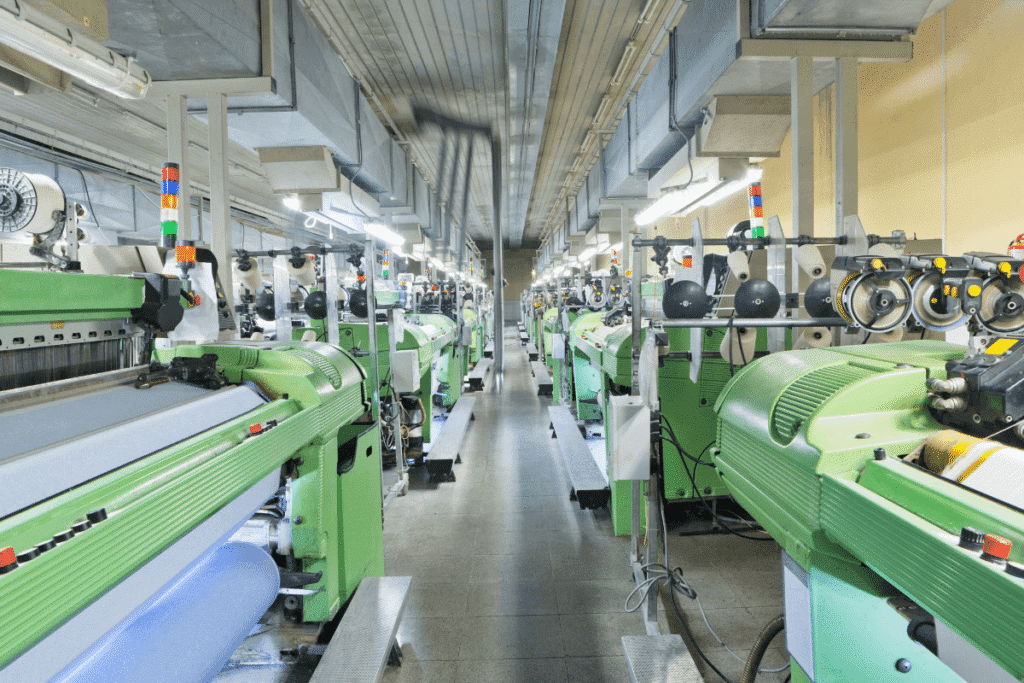

The rapid adoption of new technology has been recognised as one of the most substantial factors driving the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years. From production to processing, automation and digital tools have found a new home in the textile manufacturing process.
Today, automation in the textile industry is no longer a trend but a necessity. Labour-intensive processes are being automated, such as cutting, dyeing and quality-checking systems, which enhance efficiency and precision. To remain competitive in the global market, Indian mills and export houses are increasingly investing in these technologies.
The next giant step has been the invention and utilisation of smart fabrics in India. These fabrics can regulate temperature, resist bacteria, or even monitor health. Whether it is sports or medical equipment, Indian manufacturers are now experimenting with these advanced materials, making the nation a part of the global innovation landscape.
Moreover, the emergence of technical textiles in India, which find application in defence, construction, healthcare, automotive, etc., has presented additional avenues of revenue as well as jobs. This segment is developed, and government schemes as well as the foreign direct investment (FDI) have further fuelled this growth, making it a high-potential segment.
At textiletrendshub.com, we report on them regularly, whether that be sustainable dyeing technologies or AI-assisted design tools. Our insights reveal how innovation has remained one of the drivers of the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years.
Looking ahead, the pace of change only seems to be accelerating. As Industry 4.0 is finally being adopted by companies, the future of the Indian textile industry has never been smarter, faster, and more sustainable.
To explore how technological advancements and modernisation are shaping the future of textiles, don’t miss our detailed blog post “Smart Textiles: The Future of Fashion, Healthcare & Innovation.“
Investment and Financial Growth

Investment in the textile sector has been one of the strongest forces behind the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years. The significant boost between 2014 and 2024 in foreign direct investment (FDI) in the textile industry, as well as homegrown investment in India, was seen as a boost, particularly in technology-oriented textile experiences.
The significant step followed the rise in foreign direct investment in the textile industry as India opened its FDI policy in measures such as the “Make in India” scheme. The potential of the cost-effective and skilled labour force in India made global giants invest in Indian companies and stimulated capacity building, automation, and export growth. Simultaneously, textile hubs such as Surat, Tiruppur, and Ludhiana started attracting the attention of local and international private equity players, thereby turning into magnets of industrial growth.
Among the promising developments in the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years has been the emergence of textile start-ups. These new-age companies blend sustainability, high-tech materials and incorporation of technology to give a modern makeover to the production as well as the retail experience. Whereas the traditional mills focused on volume, the startups focused on agility, and funding flowed to them.
This wave of innovation and capital gave a great impetus to modernisation. Be it digital looms, AI-powered fabric testing, or ERP systems in factories, financial support has allowed Indian textiles to reach the limits of what they are capable of. Through its current impetus, it can be anticipated that investment in the textile sector would continue to form a pivot of India’s global ascendancy in textiles.
After all, this shifting capital scenery is a testament to the fact that the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years has not been all about the numbers but about the vision, disruption, and the confidence of investors in the future of Indian textiles.
State-Wise Growth Highlights
Regional powerhouses, such as Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Telangana, have greatly influenced the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years. These states have had their own role in influencing the direction of the sector by having favourable policies and investing in the infrastructure.
Gujarat has remained strong with Surat and Ahmedabad textile clusters supported by efficient cotton production and world-class export facilities. Tamil Nadu, known as the yarn hub, has experienced regional textile growth due to its strong spinning and garmenting base.
Maharashtra has also made huge investments in textile parks and power loom modernisation, which makes it a key player in the domestic and global marketplace. Telangana, the emerging star, has climbed up the ranks with its Kakatiya Mega Textile Park and strategic industry incentives.
State-wise growth of the textile industry illustrates how local efforts and specific industrial policies have led to overall growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years, especially in turning these regions into export-oriented textile hubs.
Year-Wise Timeline Summary (2014–2024)

When we consider the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years, it is easier to comprehend when we divide it year by year. The following is an overview of the key developments, policy changes, and export trends that defined the decade-long advancement of the industry.
🗓️2014–2016
- The government introduced the Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS).
- Focus on modernising textile machinery and boosting employment.
- A strong start in year-wise textile growth, with a steady rise in production capacity.
🗓️2017–2018
- The GST rollout initially impacted the textile supply chain but improved transparency in the long run.
- Focusing on the textile policy milestones with schemes targeting handlooms and the silk industry.
- Rise in textile exports to the U.S. and UAE.
🗓️ 2019–2020
- Ongoing implementation of the ₹6,000 crore apparel and made-ups sector package announced in 2016.
- India’s global position improved due to better compliance and product quality.
🗓️ 2021–2022
- Post-COVID recovery with the launch of the PLI scheme for man-made fibre and technical textiles.
- Remarkable export growth trends despite global disruptions.
🗓️ 2023–2024
- Heavy investment in textile parks under PM MITRA.
- Strengthened India’s role in sustainable and smart textiles.
This year-wise picture portrays a steady growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years, which is characterised by strategic reforms, rising exports, and resilient performance across sub-sectors.
Future Prospects Beyond 2024
The growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years has generated a solid base, and the future is even better. Even when we focus on the time beyond 2024, there are reasons to believe that this will be the era of innovation, sustainability, and global positioning. As the Indian government and the private sector invest in smart infrastructure, the future of the textile industry is becoming more technology-oriented and competitive at the global level.
Sustainable textile production will be one of the greatest game changers. The growth in global awareness concerning eco-friendly fabrics and ethical manufacturing processes is compelling Indian textile firms to resort to greener manufacturing processes. Whether it is waterless dyeing techniques or organic fibres, India is gearing its manufacturing systems to international environmental regulations.
Another significant change is that of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. Such tools will redesign efficiency, minimise human error and provide predictability, enabling a sustainable and smart scale for the future of the textile industry in India. With repetitive work being automated, skilled labour will be directed to design, quality control and research and development, generating new job trends.
India’s textile roadmap aims to make the country a global hub, focusing on export growth and technological upgrades. Collaborations with fashion-tech startups and global brands will be innovative but will keep traditional craftsmanship.
The growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years is just beginning. The future of the Indian textile industry is even more promising, with the textile roadmap being constantly updated in accordance with the market changes, sustainability requirements, and technology-driven solutions.
Having laid down long-term plans, long-term innovation and eco-friendly textile manufacturing will make sure that the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years will become an extended tradition.
Conclusion: 10 Years of Transformation and What Lies Ahead
The growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years does not merely demonstrate the figures, but it also portrays resilience, innovation, and global ambition. From rural handlooms to ultra-modern textile parks, the Indian textile industry has gradually evolved into a force to be reckoned with in the global arena. This phenomenal journey has been driven by government initiatives, export-friendly policies and the increasing domestic demand.
Looking back, the industry’s economic contribution has broadened enormously, both in job creation and empowerment of the local communities. As we wrap up this growth trends summary, it is obvious that the pace is not about to slacken.
Whether you’re tracking the evolution of the Indian textile sector, conducting research on future investment opportunities, or just keeping abreast of the developments in the policies, the growth of the textile industry in India in the last 10 years provides a concrete background for future indications.
To find in-depth analysis, trends, and expert-curated updates, make sure to bookmark textiletrendshub.com, your reliable source for everything textile.
For a broader view beyond the past decade, explore our in-depth blog post on the textile industry in India: its economic journey, key milestones, and future scope.

Q1. What are the key technological advancements in the Indian textile industry over the last 10 years?
In the past decade, India’s textile sector has seen a massive technological transformation—from automation in cutting, dyeing, and quality control to the emergence of smart fabrics. These innovations, including temperature-regulating and bacteria-resistant materials, are improving efficiency and placing India on the global innovation map.
Q2. How has automation changed textile production in India?
Automation has moved from being an emerging trend to a necessity in India’s textile manufacturing. It has replaced labour-intensive tasks with precision-driven processes, leading to improved speed, consistency, and competitiveness in the global market.
Q3. What is the role of smart fabrics in India’s textile growth?
Smart fabrics—those that can monitor health, control temperature, or resist bacteria—are reshaping textile innovation in India. Indian manufacturers are increasingly adopting these materials, especially in sportswear and medical textiles, positioning India as a tech-forward textile hub.
Q4. How have government policies boosted India’s textile industry from 2014 to 2024?
Policies like the Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS), the PLI scheme for technical textiles, and investments through PM MITRA have modernised the sector. These initiatives helped improve machinery, boost exports, and support sustainable growth across sub-sectors.
Q5. What impact has foreign direct investment (FDI) had on Indian textiles?
FDI has played a pivotal role in boosting India’s textile growth. Global companies, drawn by India’s skilled labour and cost advantages, invested in automation, capacity building, and export expansion, particularly under schemes like Make in India.
Q6. Which states have driven textile growth in India over the last decade?
States like Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Telangana have led regional growth. Gujarat shines with its cotton and export hubs; Tamil Nadu dominates spinning and garmenting; Maharashtra invested in textile parks; and Telangana’s Kakatiya Mega Textile Park showcases strategic planning.
Q7. What are technical textiles, and why are they important for India?
Technical textiles are materials used in sectors like defence, construction, and healthcare, beyond traditional fashion. They’ve opened new revenue and employment streams for India, backed by government support and rising demand for high-performance fabrics.
Q8. How did India’s textile sector recover post-COVID-19?
India’s textile industry bounced back with resilience, thanks to initiatives like the PLI scheme targeting man-made fibre and technical textiles. Export trends surged, and companies doubled down on smart and sustainable production practices.
Q9. What are the future trends expected in India’s textile industry beyond 2024?
The future points toward eco-friendly manufacturing, AI-driven operations, and global partnerships. From waterless dyeing to AI-powered design tools, India is evolving into a smarter, greener textile powerhouse, driven by sustainability and innovation.
Q10. How have textile startups contributed to India’s industry growth?
Startups in the textile space are blending sustainability with high-tech solutions—from smart fabrics to digital-first retail models. Unlike traditional mills, these agile players are attracting investor attention and modernising how textiles are produced and sold in India.



